Thermal conductivity of common metals, metallic elements aand Alloys


Thermal Conductivity - k - is the quantity of heat transmitted due to an unit temperature gradient, in unit time under steady conditions in a direction normal to a surface of the unit area. Thermal Conductivity - k - is used in the Fourier's equation.
| Metal, Metallic Element or Alloy | Temperature - t - (oC) | Thermal Conductivity - k - (W/m K) |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | -73 | 237 |
| ' | 0 | 236 |
| ' | 127 | 240 |
| ' | 327 | 232 |
| ' | 527 | 220 |
| Aluminum - Duralumin (94-96% Al, 3-5% Cu, trace Mg) | 20 | 164 |
| Aluminum - Silumin (87% Al, 13% Si) | 20 | 164 |
| Aluminum bronze | 0 - 25 | 70 |
| Aluminum alloy 3003, rolled | 0 - 25 | 190 |
| Aluminum alloy 2014. annealed | 0 - 25 | 190 |
| Aluminum alloy 360 | 0 - 25 | 150 |
| Antimony | -73 | 30.2 |
| ' | 0 | 25.5 |
| ' | 127 | 21.2 |
| ' | 327 | 18.2 |
| ' | 527 | 16.8 |
| Beryllium | -73 | 301 |
| ' | 0 | 218 |
| ' | 127 | 161 |
| ' | 327 | 126 |
| ' | 527 | 107 |
| ' | 727 | 89 |
| ' | 927 | 73 |
| Beryllium copper 25 | 0 - 25 | 80 |
| Bismuth | -73 | 9.7 |
| ' | 0 | 8.2 |
| Boron | -73 | 52.5 |
| ' | 0 | 31.7 |
| ' | 127 | 18.7 |
| ' | 327 | 11.3 |
| ' | 527 | 8.1 |
| ' | 727 | 6.3 |
| ' | 927 | 5.2 |
| Cadmium | -73 | 99.3 |
| ' | 0 | 97.5 |
| ' | 127 | 94.7 |
| Cesium | -73 | 36.8 |
| ' | 0 | 36.1 |
| Chromium | -73 | 111 |
| ' | 0 | 94.8 |
| ' | 127 | 87.3 |
| ' | 327 | 80.5 |
| ' | 527 | 71.3 |
| ' | 727 | 65.3 |
| ' | 927 | 62.4 |
| Cobalt | -73 | 122 |
| ' | 0 | 104 |
| ' | 127 | 84.8 |
| Copper | -73 | 413 |
| ' | 0 | 401 |
| ' | 127 | 392 |
| ' | 327 | 383 |
| ' | 527 | 371 |
| ' | 727 | 357 |
| ' | 927 | 342 |
| Copper, electrolytic (ETP) | 0 - 25 | 390 |
| Copper - Admiralty Brass | 20 | 111 |
| Copper - Aluminum Bronze (95% Cu, 5% Al) | 20 | 83 |
| Copper - Bronze (75% Cu, 25% Sn) | 20 | 26 |
| Copper - Brass (Yellow Brass) (70% Cu, 30% Zn) | 20 | 111 |
| Copper - Cartridge brass (UNS C26000) | 20 | 120 |
| Copper - Constantan (60% Cu, 40% Ni) | 20 | 22.7 |
| Copper - German Silver (62% Cu, 15% Ni, 22% Zn) | 20 | 24.9 |
| Copper - Phosphor bronze (10% Sn, UNS C52400) | 20 | 50 |
| Copper - Red Brass (85% Cu, 9% Sn, 6%Zn) | 20 | 61 |
| Cupronickel | 20 | 29 |
| Germanium | -73 | 96.8 |
| ' | 0 | 66.7 |
| ' | 127 | 43.2 |
| ' | 327 | 27.3 |
| ' | 527 | 19.8 |
| ' | 727 | 17.4 |
| ' | 927 | 17.4 |
| Gold | -73 | 327 |
| ' | 0 | 318 |
| ' | 127 | 312 |
| ' | 327 | 304 |
| ' | 527 | 292 |
| ' | 727 | 278 |
| ' | 927 | 262 |
| Hafnium | -73 | 24.4 |
| ' | 0 | 23.3 |
| ' | 127 | 22.3 |
| ' | 327 | 21.3 |
| ' | 527 | 20.8 |
| ' | 727 | 20.7 |
| ' | 927 | 20.9 |
| Hastelloy C | 0 - 25 | 12 |
| Inconel | 21 - 100 | 15 |
| Incoloy | 0 – 100 | 12 |
| Indium | -73 | 89.7 |
| ' | 0 | 83.7 |
| ' | 127 | 75.5 |
| Iridium | -73 | 153 |
| ' | 0 | 148 |
| ' | 127 | 144 |
| ' | 327 | 138 |
| ' | 527 | 132 |
| ' | 727 | 126 |
| ' | 927 | 120 |
| Iron | -73 | 94 |
| ' | 0 | 83.5 |
| ' | 127 | 69.4 |
| ' | 327 | 54.7 |
| ' | 527 | 43.3 |
| ' | 727 | 32.6 |
| ' | 927 | 28.2 |
| Iron - Cast | 20 | 52 |
| Iron - Nodular pearlitic | 100 | 31 |
| Iron - Wrought | 20 | 59 |
| Lead | -73 | 36.6 |
| ' | 0 | 35.5 |
| ' | 127 | 33.8 |
| ' | 327 | 31.2 |
| Chemical lead | 0 - 25 | 35 |
| Antimonial lead (hard lead) | 0 - 25 | 30 |
| Lithium | -73 | 88.1 |
| ' | 0 | 79.2 |
| ' | 127 | 72.1 |
| Magnesium | -73 | 159 |
| ' | 0 | 157 |
| ' | 127 | 153 |
| ' | 327 | 149 |
| ' | 527 | 146 |
| Magnesium alloy AZ31B | 0 - 25 | 100 |
| Manganese | -73 | 7.17 |
| ' | 0 | 7.68 |
| Mercury | -73 | 28.9 |
| Molybdenum | -73 | 143 |
| ' | 0 | 139 |
| ' | 127 | 134 |
| ' | 327 | 126 |
| ' | 527 | 118 |
| ' | 727 | 112 |
| ' | 927 | 105 |
| Monel | 0 – 100 | 26 |
| Nickel | -73 | 106 |
| ' | 0 | 94 |
| ' | 127 | 80.1 |
| ' | 327 | 65.5 |
| ' | 527 | 67.4 |
| ' | 727 | 71.8 |
| ' | 927 | 76.1 |
| Nickel - Wrought | 0 – 100 | 61 – 90 |
| Cupronickel 50 -45 (Constantan) | 0 - 25 | 20 |
| Niobium (Columbium) | -73 | 52.6 |
| ' | 0 | 53.3 |
| ' | 127 | 55.2 |
| ' | 327 | 58.2 |
| ' | 527 | 61.3 |
| ' | 727 | 64.4 |
| ' | 927 | 67.5 |
| Osmium | 20 | 61 |
| Palladium | 75.5 | |
| Platinum | -73 | 72.4 |
| ' | 0 | 71.5 |
| ' | 127 | 71.6 |
| ' | 327 | 73.0 |
| ' | 527 | 75.5 |
| ' | 727 | 78.6 |
| ' | 927 | 82.6 |
| Plutonium | 20 | 8.0 |
| Potassium | -73 | 104 |
| ' | 0 | 104 |
| ' | 127 | 52 |
| Red brass | 0 - 25 | 160 |
| Rhenium | -73 | 51 |
| ' | 0 | 48.6 |
| ' | 127 | 46.1 |
| ' | 327 | 44.2 |
| ' | 527 | 44.1 |
| ' | 727 | 44.6 |
| ' | 927 | 45.7 |
| Rhodium | -73 | 154 |
| ' | 0 | 151 |
| ' | 127 | 146 |
| ' | 327 | 136 |
| ' | 527 | 127 |
| ' | 727 | 121 |
| ' | 927 | 115 |
| Rubidium | -73 | 58.9 |
| ' | 0 | 58.3 |
| Selenium | 20 | 0.52 |
| Silicon | -73 | 264 |
| ' | 0 | 168 |
| ' | 127 | 98.9 |
| ' | 327 | 61.9 |
| ' | 527 | 42.2 |
| ' | 727 | 31.2 |
| ' | 927 | 25.7 |
| Silver | -73 | 403 |
| ' | 0 | 428 |
| ' | 127 | 420 |
| ' | 327 | 405 |
| ' | 527 | 389 |
| ' | 727 | 374 |
| ' | 927 | 358 |
| Sodium | -73 | 138 |
| ' | 0 | 135 |
| Solder 50 - 50 | 0 - 25 | 50 |
| Steel - Carbon, 0.5% C | 20 | 54 |
| Steel - Carbon, 1% C | 20 | 43 |
| Steel - Carbon, 1.5% C | 20 | 36 |
| ' | 400 | 36 |
| ' | 122 | 33 |
| Steel - Chrome, 1% Cr | 20 | 61 |
| Steel - Chrome, 5% Cr | 20 | 40 |
| Steel - Chrome, 10% Cr | 20 | 31 |
| Steel - Chrome Nickel, 15% Cr, 10% Ni | 20 | 19 |
| Steel - Chrome Nickel, 20% Cr, 15% Ni | 20 | 15.1 |
| Steel - Hastelloy B | 20 | 10 |
| Steel - Hastelloy C | 21 | 8.7 |
| Steel - Nickel, 10% Ni | 20 | 26 |
| Steel - Nickel, 20% Ni | 20 | 19 |
| Steel - Nickel, 40% Ni | 20 | 10 |
| Steel - Nickel, 60% Ni | 20 | 19 |
| Steel - Nickel Chrome, 80% Ni, 15% Ni | 20 | 17 |
| Steel - Nickel Chrome, 40% Ni, 15% Ni | 20 | 11.6 |
| Steel - Manganese, 1% Mn | 20 | 50 |
| Steel - Stainless, Type 304 | 20 | 14.4 |
| Steel - Stainless, Type 347 | 20 | 14.3 |
| Steel - Tungsten, 1% W | 20 | 66 |
| Steel - Wrought Carbon | 0 | 59 |
| Tantalum | -73 | 57.5 |
| ' | 0 | 57.4 |
| ' | 127 | 57.8 |
| ' | 327 | 58.9 |
| ' | 527 | 59.4 |
| ' | 727 | 60.2 |
| ' | 927 | 61 |
| Thorium | 20 | 42 |
| Tin | -73 | 73.3 |
| ' | 0 | 68.2 |
| ' | 127 | 62.2 |
| Titanium | -73 | 24.5 |
| ' | 0 | 22.4 |
| ' | 127 | 20.4 |
| ' | 327 | 19.4 |
| ' | 527 | 19.7 |
| ' | 727 | 20.7 |
| ' | 927 | 22 |
| Tungsten | -73 | 197 |
| ' | 0 | 182 |
| ' | 127 | 162 |
| ' | 327 | 139 |
| ' | 527 | 128 |
| ' | 727 | 121 |
| ' | 927 | 115 |
| Uranium | -73 | 25.1 |
| ' | 0 | 27 |
| ' | 127 | 29.6 |
| ' | 327 | 34 |
| ' | 527 | 38.8 |
| ' | 727 | 43.9 |
| ' | 927 | 49 |
| Vanadium | -73 | 31.5 |
| ' | 0 | 31.3 |
| ' | 427 | 32.1 |
| ' | 327 | 34.2 |
| ' | 527 | 36.3 |
| ' | 727 | 38.6 |
| ' | 927 | 41.2 |
| Zinc | -73 | 123 |
| ' | 0 | 122 |
| ' | 127 | 116 |
| ' | 327 | 105 |
| Zirconium | -73 | 25.2 |
| ' | 0 | 23.2 |
| ' | 127 | 21.6 |
| ' | 327 | 20.7 |
| ' | 527 | 21.6 |
| ' | 727 | 23.7 |
| ' | 927 | 25.7 |
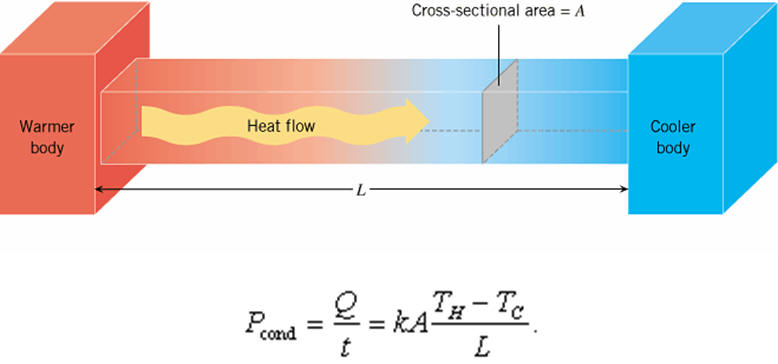
A noninsulated uniform rod positioned between two walls of constant but different temperature. The finite-difference representation employs four interior nodes. Where T =temperature ( C), x =distance along the rod (m), h′ =a heat transfer coefficient between the rod and the surrounding air (m−2), and T a = the air temperature ( C). Since one iron rod is twice the diameter of the other, it has four times the cross-sectional area, and thus should conduct heat four times as fast. It also has, however, four times the mass of the other rod, and so requires four times as much heat to raise its temperature by the same amount.
If one end of a metal rod is at a higher temperature, then energy will be transferred down the rod toward the colder end because the higher speed particles will collide with the slower ones with a net transfer of energy to the slower ones.
Alloys - Temperature and Thermal Conductivity
Temperature and thermal conductivity for
- Hastelloy A
- Inconel
- Nichrome V
- Kovar
- Advance
- Monel
alloys:
Related Topics
- Material Properties - Material properties for gases, fluids and solids - densities, specific heats, viscosities and more
Related Documents
Heat Transfer In Metal Rodgers
- Aluminum - Radiation Heat Emissivity - Radiation heat emissivity of unoxidized, oxidized and polished aluminum
- Aluminum Alloys - Mechanical Properties - Mechanical properties of aluminum alloys - tensile strength, yield strength and more
- Butane - Thermal Conductivity - Online calculators, figures and tables showing thermal conductivity of liquid and gaseous butane, C4H10, at varying temperarure and pressure, SI and Imperial units
- Conductive Heat Transfer - Heat transfer takes place as conduction in a solid if there is a temperature gradient
- Electrode Potential and Galvanic Corrosion - Introduction to electro chemical series and corrosion of metals
- Ethane - Thermal Conductivity - Online calculator, figures and table showing thermal conductivity of ethane, C2H6, at varying temperature and pressure - Imperial and SI Units
- Ethylene - Thermal Conductivity - Online calculator, figures and table showing thermal conductivity of ethylene, also called ethene or acetene, C2H4, at varying temperature and pressure - Imperial and SI Units
- Food - Thermal Conductivity - Thermal conductivity of selected foodstuff
- Hydrogen - Thermal Conductivity - Online calculator, figures and table showing thermal conductivity of hydrogen, H2, at varying temperature and pressure - Imperial and SI Units
- Metal Alloys - Specific Heats - Specific heat of metal alloys like brass, bronze and more
- Metals - as Liquids - Boiling points and specific heat of liquid metals
- Metals - Boiling Temperatures - Metals and their boiling temperatures
- Metals - Latent Heat of Fusion - Metals and their latent heat of fusion
- Metals and Alloys - Densities - Density of some common metals, metallic elements and alloys - aluminum, bronze, copper, iron and more ..
- Metals and Alloys - Melting Temperatures - Melting temperatures of common metals and alloys
- Metals and Corrosion Resistance - Common metals and their corrosion resistance to aggressive fluids like acids, bases and more
- Nitrogen - Thermal Conductivity - Online calculator, figures and tables showing thermal conductivity of nitrogen, N2, at varying temperarure and pressure, SI and Imperial units
- Plastics - Thermal Conductivity Coefficients - Thermal conductivity of plastics
- Poisson's Ratio for Metals - Some metals and their Poisson's Ratio
- Propane - Thermal Conductivity - Online calculator, figures and tables showing thermal conductivity of liquid and gaseous propane at varying temperarure and pressure, SI and Imperial units
- Specific Heat of some Metals - Specific heat of commonly used metals like aluminum, iron, mercury and many more - imperial and SI units
- Temperature - Introduction to temperature - including Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin and Rankine definitions - an online temperature converter
- Temperature and Strength of Metals - Influence of temperature on strength of metals
- Thermal Conductivities of Heat Exchanger Materials - Typical heat exchanger materials and their thermal conductivities
- Thermal Conductivities of some common Liquids - Some fluids and their thermal conductivities
- Thermal Conductivity Conversion Factors - Convert between thermal conductivity units
- Thermal Conductivity of some selected Materials and Gases - Thermal conductivity of some selected gases, insulation products, aluminum, asphalt, brass, copper, steel and other common materials
- Thermal Conductivity Online Converter - Convert thermal conductivities
- Thermal Expansion of Metals - Thermal expansion of some common metals
- Thermal Resistivity and Conductivity - Thermal resistivity and conductivity
- Water - Thermal Conductivity - Figures and tables showing thermal conductivity of water (liquid and gas phase) with varying temperature and pressure, SI and Imperial units
Tag Search
Heat Transfer Using Metal Rod Wax And Pins
- en: thermal conductivity metals
- es: metales de conductividad térmica
- de: Wärmeleitfähigkeit Metalle